- Home
- Rubber Info
Rubber Material & Capabilities FAQs
- What is Rubber?
-
What is Rubber?
Rubber is a highly elastic and flexible polymer material that can return to its original shape after being stretched, compressed, or deformed.
It can be natural or synthetic, and it's widely used in industrial, automotive, consumer, medical, and construction applications due to its durability, resilience, sealing ability, and insulation properties.Types of Rubber
- Natural Rubber (NR)
Source: Harvested from the sap (latex) of rubber trees (Hevea brasiliensis).
Features: High tensile strength, excellent elasticity, abrasion resistance.
Common Uses: Tires, hoses, gaskets, rubber bands. - Synthetic Rubber
Made from petroleum-based monomers. Common types include:
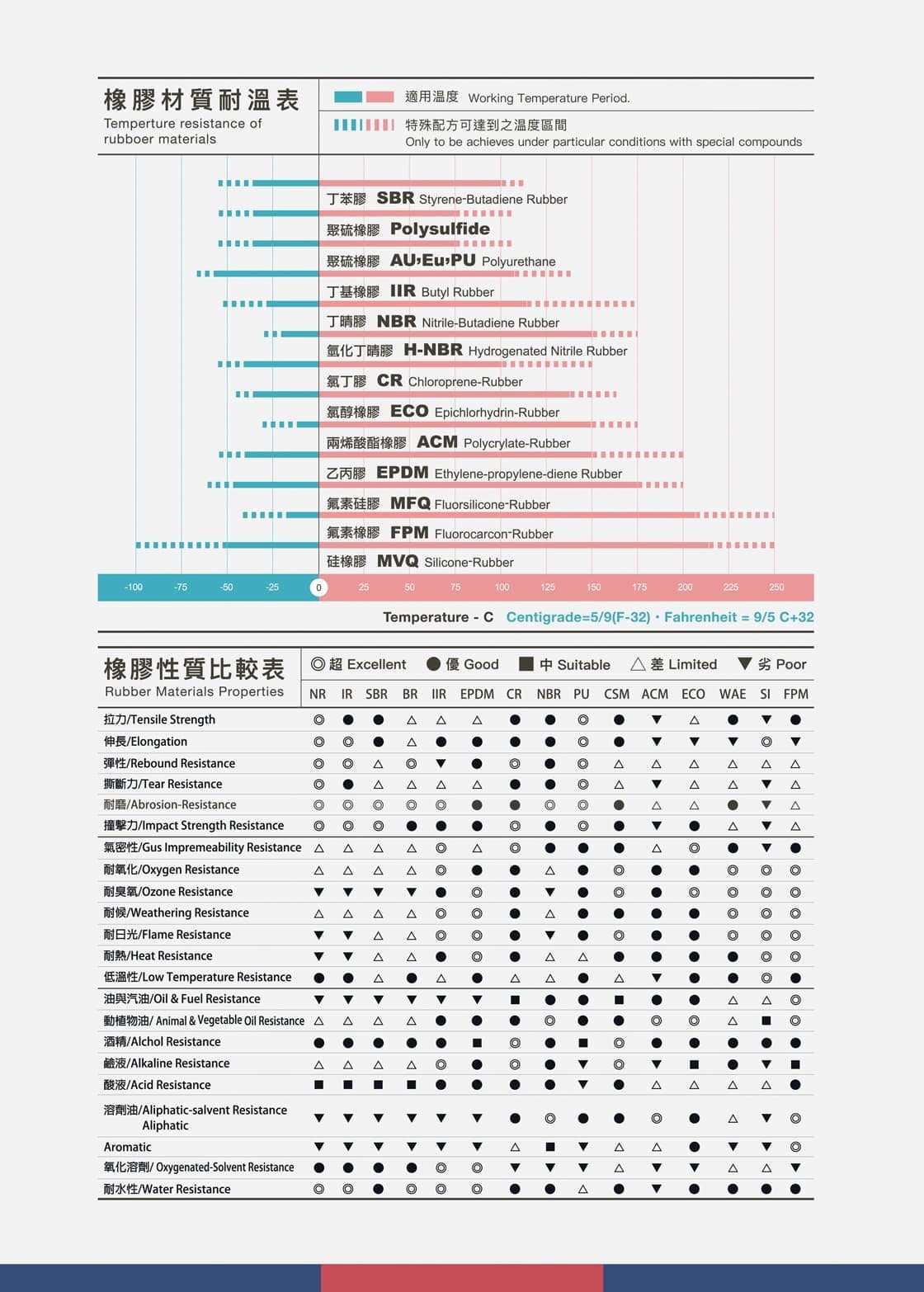
請左右← →滑動看完整表格Type Abbreviation Key Properties Applications Nitrile NBR Oil and fuel resistance Seals, gaskets, fuel hoses EPDM EPDM Weather and ozone resistance Automotive seals, roofing Silicone VMQ High-temperature and food-safe Medical devices, kitchenware Neoprene CR Weather and chemical resistance Wetsuits, cable jackets Viton® FKM High chemical and heat resistance Aerospace, chemical seals
Key Properties of Rubber
Elasticity: Can stretch and return to its original shape.
Waterproof: Excellent water resistance.
Electrical Insulation: Non-conductive and safe for electrical use.
Durability: Withstands abrasion, weathering, and vibration.
Chemical Resistance: Varies by type; some rubbers resist oil, acid, and alkali.Common Applications
Automotive: Tires, belts, bushings, seals, hoses.
Industrial: Conveyor belts, machine mounts, anti-vibration pads.
Medical: Gloves, tubing, stoppers.
Consumer: Footwear, sports goods, grips.
Construction: Expansion joints, waterproof membranes, insulation. - Natural Rubber (NR)
- Temperature Resistance Of Rubber Materials & Rubber Materials Properties
-